How to best Identify Different Types of Fuse
Table of Contents
ToggleIn the intricate world of electrical systems, fuses stand as guardians, ensuring the safety and reliability of circuits. Understanding the different types of fuses is crucial for selecting the right protection for various applications. This article delves into the diverse universe of fuses, highlighting key types that play pivotal roles in different industries.
The fuse is made according to the rating and according to the voltage the fuse is divided into two categories. let us now learn about different types of fuse.
- Low Voltage Fuse
- High Voltage Fuse
Different types of fuse for Low Voltage
1. Semi Enclosed Rewireable Fuse
A few different types of fuses include a semi enclosed rewirable fuse, which is also an electrical fuse. These types of electric fuse consists of a porcelain base carrying the fixed contacts, to which one side incoming and other side outgoing live or phase wires are connected.
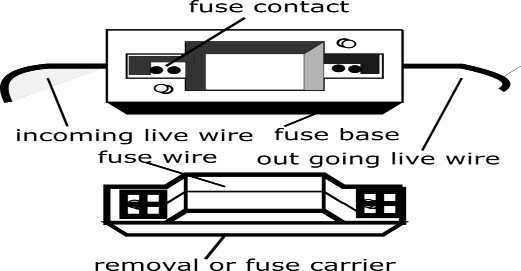
The second part of this fuse unit is called fuse carrier. This part is also called protection zone. Two copper contacts are placed at standard distances. When the fuse carrier is inserted into the base, the circuit is complete and current starts flowing towards the load.
When a fault occurs in the circuit, the current flows more than the standard rating of the fuse element, due to which the fuse wires melt due to excessive heat and break the circuit.
In this type of fuse carrier, the fuse wire is made from lead, copper or an alloy of lead and tin. In this way, the circuit remains safe
Advantage of Electric Fuse
- One can easily change this type of fuse wire at any time. ed.
- Even if any part of this type of fuse gets destroyed, this part can be easily replaced.
Disadvantages of Elecric Fuse
- The fuse wire used in this type of fuse is always of wrong size and capacity.
- In this type of safety fuse unit, the fuse wire keeps getting damaged due to continuous heating effect and oxidation.
- This type of fuse wire has limited ability to break or melt.
- This type of electrical fuse lacks discrimination. Means a fuse of 60A will discriminate with a fuse of 30A,but not with a fuse of 55A
- It is very difficult to accurately calibrate a fuse wire.
It is often used in low and medium voltage circuits due to simplicity and chipness.
2. Cartridge electric fuse
Cartridge electric fuse is another type of fuse under different types of fuse. These types of fuse wire unit are completely closed in which the fuse wire is attached between both and the metal sealed cap and the pure quartz powder is filled around the fuse wire.
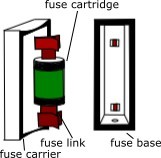
This powder dissipates the heat generated in the fuse wire by conduction and convention.Cartridge type fuses are designed for low voltage, high voltage and minor application functions. Its fuse link, which fits into the fuse carrier, can be replaced very easily.
For lower current ratings, the fuse link has a single wire, while for higher ratings the fuse link has several parallel wires connected. This type of fuse element wire is usually silver or silver plated copper.
Single element wire up to 10A or less rating is used in this fuse. But for higher rating, strips with one or more section of reduced cross-sectional area are used in this fuse. But for higher rating, strips with one or more section of reduced cross-sectional area are used.
The body of this type of fuse is made of ceramic and glass which maintains good insulation even in very harsh conditions. Recently glass reinforced plastic is used in it. It is available in standard ratings of 6,16,32 and 63 amps. The biggest advantage is that their operation is reliable, with them coordination and discrimination are achieved to a reasonable extent.
High Rupturing Capacity Cartridge electric Fuse
This is another different types of fuse. The outer part of this type of fuse device is made of ceramic. Its structure is shown in the figure, which is in cylindrical form. Brass caps are attached at both the ends of this cylindrical part, and fuse wire is attached to both the caps.
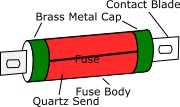
Its cylindrical part is filled with quartz sand. When there is a fault in a circuit, the fault current starts flowing through this fuse wire in the circuit, when the current increases above a certain value, the fuse wire inside the fuse gets heated and melts.
During a fault, a flash is generated inside the fuse, but the quartz sand immediately extinguishes this generated flash. Quartz sand acts as a fire extinguisher. Quartz sand also protects the silver element from oxidation. The fuse wire mostly used in this is made of silver or copper.
In this, the fuse element consists of two or more sections of wire connected through a tin joint. Limiting the temperature of the fuse using a tin joint. Preferred rating of HRC fuse are 6,10,16,25,30,50,63A etc. According to their breaking capacity, HRC fuses are divided into four different classes.
Cetegory
Class 1AC & DC
Class 2AC & DC
Class 3 AC only
Class 4 AC only
Prospective Fault Current in KA
10
33
46
80
Power Factor Not Exceeding
0.3
0.3
0.15
0.15
Important Characteristics of HRC electric Fuse are
- I^{2}t The characteristics mean total ampere square-seconds and pre-arcing ampere square-seconds. This characteristic helps in determining the maximum amount of energy that can be released into the fuse under protection.
- HRC fuse has very fast operation. This fuse interrupts the short circuit current before it reaches its maximum value.
- HRC fuses do not suffer from oxidation problems because the fuse wire is covered inside quartz sand, which is not exposed to the atmosphere.
- HRC fuses have inverse time-current, making them suitable for overload protection.
Advantages HRC fuse
- it is cheap
- Their working capacity remains the same continuously
- Their operation is very good on both high and low currents.
- The flashing does not come out because this fuse is completely enclosed in a porcelain vessel.
- It has high permeability.
- No maintenance is required.
- Its operation is quick and sure.
- There is almost no chance of oxidation of the fuse wire.
Disadvantages of HRC electric Fuse
- Once operated, it has to be replaced.
- This causes overheating of adjacent contacts or components and damage.
- it is not repairable.
High Voltage electric Fuse are Three Type
1. High Voltage HRC Fuse
High voltage HRC fuse and low voltage HRC cartridge fuse are almost similar. But in a high voltage fuse, the fuse wire is coiled into a helix shape to reduce corona losses.
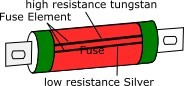
A high voltage fuse has two parallel fuse wires, one of low resistance and the other of high resistance.
The low resistance fuse wire carries normal current and when it flows to short circuit, the entire current flows through another single wire with higher resistance, which limits the short circuit current and ultimately breaks the circuit.
The low resistance fuse wire is made of silver and the high resistance wire is made of tungsten wire.
2. Expulsion electric Fuse
This fuse also comes in the category of different types of fuse. This type of fuses used in high voltage circuits have a small element tinned or tinned copper wire in series with a flexible braid.
These items are attached to a fuse carrier consisting of organic material inside a tube, which is usually attached at the top with a delicate diaphragm and includes a linear section of gas-evolved material such as fiber.
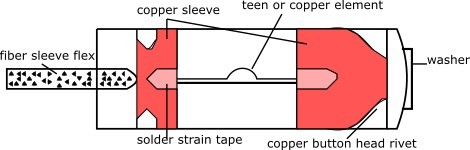
These items are fused with organic material in a fuse carrier that includes the inside of the tube, which usually has a delicate diaphragm attached at the top and includes a linear section of gas-evolved material such as fiber.
This type of fuse carrier is kept inclined vertically. When the fuse wires melt during operation, the release of spring tension locks a latch, allowing the fuse carrier to swing downwards by the force of gravity.
This causes the electrical isolation within extinguished the arc, disrupting the fabric sleeves with relatively low currents around the element, but at high currents the sleeve burst and the arc is extinguished within the linear of the gas forming material.
Fuses are capable of breaking a wide range of fault currents. These type of fuses are used for outdoor in three-phase circuits with current and voltage ratings up to 100A and 72KV. Their breaking capacity is limited to about 150MVA.
3. Liquid electric Fuse
Many fuses had their arc extinguished easily in liquid, and this is the principle used in current liquid fuses. This fuse is inside a glass tubular body which is mounted vertically. Silver wire located near the top of the tube. This element is kept under tension from the lower part of the fuse by means of a spring.
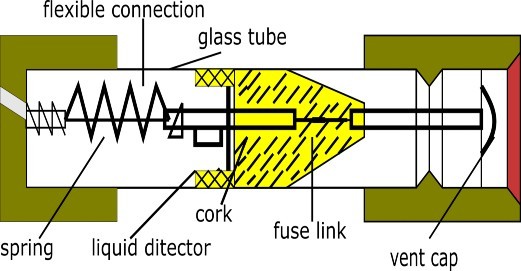
The tube is filled with an arc-extinguishing fluid, usually a hydrocarbon. When the element melts during operation, the spring falls off and the arc is extinguished in the liquid.
Such fuses are used only outside, and provision is also made for their removal and conversion from the group to their mounting. These are mostly used to protect 11KV or 33KV pole mounted distribution transformers in rural areas.
I am an engineer in a government department and also a blogger. I write posts on topics related to electrical and electronics engineering.
