Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Table of Contents
ToggleThere has been a significant change in the global automotive industry towards electric cars (EVs) as a means of pursuing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Electric vehicle charging stations have become a crucial piece of infrastructure that is necessary for the broad adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) as governments, corporations, and individuals see the benefits of these vehicles more and more.
Evolution of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations:
The inception of electric car development is when the idea for charging stations for these vehicles first emerged. But major growth and innovation in charging infrastructure did not occur until recently.
Globally, the number of charging networks has increased due to the rise in popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) caused by improvements in battery technology, environmental concerns, and government incentives.
The majority of early electric vehicle charging stations offered only sluggish charging, which frequently took several hours to fully recharge a vehicle’s battery.
However, faster charging options, including as DC fast chargers and Level 2 chargers, have been developed as a result of technological breakthroughs, greatly cutting down on charging periods and improving convenience for EV owners.
Importance of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations:
Stations for charging electric vehicles are essential for quickening the shift to environmentally friendly transportation. It is possible to comprehend their significance from a number of angles:
Range Anxiety Mitigation
The worry that an EV won’t have enough battery life to reach a charging station, or range anxiety, has been a major obstacle to EV adoption. An extensive network of charging stations allays this worry, boosting consumer trust in electric vehicles.
Environmental Impact:
Charging stations help lower greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution linked to conventional gasoline-powered automobiles by encouraging the wider use of electric vehicles.
Mitigating climate change and enhancing urban air quality require a shift towards greener transportation.
Economic Growth:
The construction of infrastructure for charging electric vehicles contributes to economic growth by generating employment, encouraging investment in clean energy technology, and encouraging innovation in the automotive industry. It also improves energy security and resilience by lowering dependency on imported fossil fuels.
Grid Integration and Renewable Energy:
Stations for charging electric vehicles present potential for renewable energy sources like solar and wind electricity to be integrated into the grid.
An energy ecology that is more sustainable is made possible by smart charging systems, which balance electricity demand and allow for the best possible use of renewable energy sources.
Challenges Facing Electric Vehicle Charging Stations:
Despite their importance, electric vehicle charging stations have a number of issues that must be resolved to guarantee their broad use and efficacy:
Infrastructure Investment:
Both the public and commercial sectors must make significant investments in order to expand the infrastructure for charging. To overcome financial obstacles and expedite the deployment of infrastructure, businesses, utilities, and governments must work together.
Interoperability and Standards:
For EV consumers, interoperability is an issue due to the proliferation of many charging standards and protocols. Ensuring seamless charging experiences and promoting EV adoption require the establishment of universal standards and interoperable charging technologies.
Grid Capacity and Stability:
Upgrades to the electrical system are required to handle higher loads due to the charging stations’ growing demand for electricity. Smart charging technology and grid modernization initiatives are required to overcome stability concerns and capacity restrictions.
Urban Planning and Accessibility:
Particularly in crowded regions and underprivileged groups, efficient urban design is necessary to guarantee fair access to charging infrastructure.
To encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) among a variety of demographic groups, charging stations must be strategically placed in public areas, businesses, and residential locations.
Future Prospects and Innovations:
Future developments and inventions targeted at resolving issues and improving user experience point to a bright future for electric vehicle charging stations:
Ultra-Fast Charging Technologies:
High-power DC chargers and solid-state batteries are two examples of innovations in ultra-fast charging technologies that promise to significantly shorten charging times and improve convenience for electric vehicle drivers.
Wireless Charging:
With the ability to charge EVs without the need for physical connections, wireless charging technology has the potential to completely transform the charging process and provide EV owners with more convenience and freedom.
Energy Storage Integration:
By providing backup power during times of high demand and reducing grid impact, the integration of energy storage devices with charging infrastructure can improve the stability and resilience of the grid.
Smart Grid Solutions:
Smart grid solutions, Demand response, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration, and advanced energy management systems are examples of smart grid technologies that increase the use of renewable energy sources, balance grid loads, and optimize charging operations.
Understanding the Costs of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
The cost of electric car charging stations is an important issue that needs to be addressed as the world moves closer to using electric vehicles (EVs). These charging stations are the foundation of the electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, giving drivers the means to conveniently and effectively power their cars.
But as stakeholders—governments, companies, and consumers—manage the shift to electric mobility, it is critical that they comprehend the different elements that affect the cost of setting up and maintaining these charging stations.
We will examine the installation costs, operating costs and financial implications of developing and maintaining charging infrastructure
Installation Costs:
Electric vehicle charging station installation costs can differ greatly based on a number of factors, including:
Charger Type: Installation costs vary depending on the type of charger—Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast chargers, for example. Standard residential outlets are used by Level 1 chargers, which are less expensive to install but have slower charging rates.
On the other hand, installing Level 2 chargers is more expensive since they need specific electrical circuits and have greater power capacities.
DC fast chargers, which are able to provide quick charging, usually come with greater installation costs and significant infrastructure requirements.
Site Preparation: Installation costs can be greatly impacted by site-specific variables, such as the availability of electrical infrastructure, site layout, permit requirements, and building concerns.
The cost of upgrading electrical systems, digging trenches for cable installations, and adhering to local building laws and requirements can all add up.
Networking and Connectivity: Installation costs can be greatly impacted by site-specific variables, such as the availability of electrical infrastructure, site layout, permit requirements, and building concerns.
The cost of upgrading electrical systems, digging trenches for cable installations, and adhering to local building laws and requirements can all add up.
Ancillary Equipment: For safe and convenient charging station installations, extra elements like landscaping, lighting, signage, and parking lot improvements could be required. The entire installation budget should account for these supplementary charges.
Operational Costs:
Electric vehicle charging stations include continuing operating costs in addition to the initial installation costs. These costs include:
Electricity Costs: The cost of the electricity used during charging sessions is the main operational expense of charging stations.
There are several charging stations that offer different pricing systems, including as time-based costs, flat rates, or kWh pricing models. Charge rates, user demand patterns, and local utility rates are some of the variables that affect the price of electricity.
Maintenance and Service: To guarantee optimum performance and dependability, charging equipment requires routine maintenance and servicing.
Cleaning, software upgrades, equipment inspections, and repairs are a few examples of maintenance duties. To prevent downtime and guarantee customer happiness, budgeting for maintenance costs is essential.
Network Subscription Fees: The use of software platforms, billing systems, and charging network services may require charging station operators to pay subscription fees.
These charges go toward covering the total operational expenses of overseeing the infrastructure for charging and ensuring smooth user experiences.
Customer Support and Administration: Operational overhead includes executing administrative duties, processing payments, maintaining user accounts, and offering customer support.
Optimizing the usability of charging infrastructure and guaranteeing user happiness require effective administration and customer service procedures.
Economic Considerations:
A number of economic considerations affect investment decisions and the feasibility of deploying charging infrastructure beyond the direct expenses of setting up and running electric vehicle charging stations:
Return on Investment (ROI):
A number of variables need to be taken into account when estimating the possible return on investment (ROI) of charging station installations, including usage patterns, income creation, cost savings (such as gasoline savings for EV owners), and equipment longevity. Stability and long-term profitability rely on striking a balance between initial expenses and income sources.
Business Models:
Operators of charging stations can choose from a variety of revenue strategies, such as pay-per-use, subscription, private, public, and hybrid approaches.
Profitability and competitiveness in the market are influenced by the distinct revenue streams, cost structures, and market dynamics found in each business model.
Policy Incentives:
Investments in charging infrastructure can have a big financial impact from government grants, tax credits, incentives, and regulation.
To encourage the widespread use of electric vehicles and assist offset the cost of initial investments, infrastructure development initiatives, electricity rates, and installation cost subsidies can be implemented.
Market Demand and Competition:
Consumer preferences, competitive dynamics, and market demand for EV charging services all affect how feasible and profitable it is to construct charging stations. To make wise investment selections, one must comprehend consumer behavior, market trends, and emerging technology.
What are Solar Charging Stations for electric vehicles
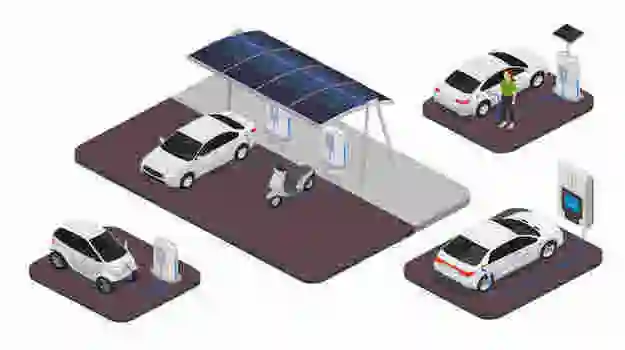
The incorporation of renewable energy sources has gained importance as the globe transitions to more environmentally friendly modes of transportation.
An important step in the right direction is the availability of solar charging stations for electric cars (EVs), which provide a clean, effective, and ecologically responsible way to power EVs.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, which use sunshine to create electricity, are installed in solar charging stations for electric cars.
After that, electric cars are charged using this renewable energy, which offers a more environmentally friendly option to traditional charging techniques that rely on grid electricity.
The capacity and size of solar charging stations can vary, from huge facilities for public and commercial charging needs to modest installations for domestic use.
Benefits of Solar Charging Stations:
Clean Energy Generation: By utilizing the sun’s abundant and sustainable energy, solar charging stations help minimize greenhouse gas emissions linked to transportation and decrease dependency on fossil fuels. Solar charging stations help to improve air quality and mitigate climate change by utilizing renewable energy sources.
Energy Independence: By producing electricity locally, solar charging stations lessen reliance on centralized power networks and erratic energy markets, so promoting energy independence. Reliability and resilience are increased by this decentralized method, particularly in isolated or off-grid areas.
Cost Savings: Solar charging stations offer long-term cost benefits through lower electricity bills and operating expenses, even if their initial installation costs may be higher than those of standard grid-connected chargers. Infrastructure made of solar panels pays for itself over time by offering a long-term, cost-effective charging option.
Grid Relief and Peak Demand Reduction: Because solar charging stations lower peak demand during the day, they lessen the burden on the electrical grid. Solar charging stations, especially in places where EV adoption is significant, contribute to grid stability and reliability by producing electricity locally and offsetting grid usage.
Promotion of Renewable Energy: Solar charging stations act as outward representations of the use of renewable energy, fostering awareness and the shift to cleaner energy sources. They encourage the adoption of sustainable practices and technologies by businesses, communities, and policymakers.
Challenges and Considerations:
Solar charging stations offer many advantages, but there are certain drawbacks and things to keep in mind as well:
Intermittent Nature of Solar Power: Since solar charging stations generate their energy from sunshine, they are vulnerable to daily variations in solar irradiation as well as weather.
Batteries and other energy storage devices can be needed to store extra energy for charging at night or during times when there is less sunlight.
Space and Siting Requirements: Installing PV panels on solar charging stations requires enough space, which might be difficult in metropolitan areas where there is a shortage of available land.
In order to optimize the efficiency of charging stations and maximize solar energy harvest, careful site selection, orientation, and integration into the existing infrastructure are crucial.
Initial Investment and Financing: Solar charging station installation can have substantial up-front expenditures for PV panels, inverters, mounting frameworks, and electrical infrastructure.
Important factors to take into account when developing a project are finding funding, overcoming legal restrictions, and determining economic viability.
Technical Integration and Compatibility: To guarantee compatibility, efficiency, and safety when integrating solar PV systems with EV charging equipment, meticulous planning and coordination are needed.
To provide smooth charging experiences, technical issues with electrical connectivity, system architecture, and communication protocols must be resolved.
electric vehicles charging station business in india
India is poised for a revolution in transportation as it welcomes the shift to electric vehicles (EVs) in an effort to improve energy security, tackle air pollution, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. As the foundation of the EV infrastructure, the installation of electric vehicle charging stations is essential to this transition.
The Growing Demand for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure:
The need for infrastructure for charging electric vehicles is rising quickly due to the government of India’s aggressive goals to electrify the country’s automobile fleet. The following are some of the causes that are accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles:
Government Incentives and Policies: The Indian government has implemented a number of policies and incentives to encourage the use of electric vehicles, such as tax breaks, subsidies for EV purchases, and financial support for the construction of charging infrastructure.
The expansion of the EV ecosystem is being accelerated by programs like the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) and the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) plan.
Environmental Imperatives: India’s cities suffer greatly from air pollution, which is primarily caused by emissions from moving cars. Making the switch to clean energy-powered electric vehicles offers a chance to reduce air pollution and enhance public health outcomes.
Technological Advancements: Developments in electric vehicle design, infrastructure for charging, and battery technology have reduced the cost, increased utility, and increased market appeal of EVs.
Consumer interest and acceptance of electric car models are being propelled by their increasing availability, performance, and range.
Opportunities for Electric Vehicle Charging Station Business:
India’s electric car charging station market offers a wide range of prospects for stakeholders, entrepreneurs, and investors.
Market Growth Potential: The need for infrastructure for charging electric vehicles is expected to increase due to India’s sizable and quickly growing industry. Investing in networks of charging stations provides a first-mover advantage and a chance to take a sizable chunk of the developing market.
Diverse Business Models: There are a number of business models that electric vehicle charging station owners can investigate, such as community-based charging hubs, workplace charging options, private charging stations for commercial fleets, and public charging networks.
Enhancing business resilience and profitability can be achieved through diversifying revenue streams and serving various customer segments.
Partnerships and Collaboration: To accelerate the implementation of charging infrastructure, cooperation between governmental organizations, utilities, automakers, real estate developers, and technological companies is crucial.
Access to resources, knowledge, and market opportunities can be facilitated by forming strategic alliances and partnerships.
Value-added Services: Value-added services like solar integration, energy management programs, battery swapping services, and digital payment systems could be provided in addition to standard charging services. Developing unique products and improving user experience can increase income and foster client loyalty.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite the promising prospects, the electric vehicle charging station business in India faces several challenges:
Infrastructure Investment: When it comes to purchasing equipment, paying for installation, and integrating the grid, the initial capital outlay needed to implement charging infrastructure can be high. For a business to be viable, obtaining funding and implementing strategies that are cost-effective are essential.
Regulatory Framework: Operators of charging stations face difficulties related to technical standards, licensing requirements, regulatory ambiguity, and power laws.
To encourage investment confidence and market expansion, it is necessary to have expedited clearance procedures, clear and consistent policies, and regulatory backing.
Grid Integration and Stability: Careful planning is necessary to assure grid stability, dependability, and load control when integrating electric vehicle charging infrastructure with the power system.
In order to minimize grid impacts and maximize efficiency, it is imperative to balance electricity demand, enhance grid capacity, and optimize charging patterns.
User Awareness and Adoption: To promote EV adoption, it is essential to inform consumers about the advantages of EVs, debunk myths regarding range anxiety and the availability of charging stations, and enhance accessibility and convenience.
Promoting electric mobility requires developing public awareness campaigns, providing incentives, and improving user experience.
electric vehicles charging station companies in india
India is making rapid progress toward electric mobility as a result of coordinated efforts to lower emissions, fight air pollution, and improve energy security.
Companies that operate electric car charging stations are essential to this shift because they build the infrastructure required to facilitate the widespread use of electric vehicles (EVs).
Tata Power:
One of the biggest integrated power utilities in India, Tata Power is a major force in the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles. Under the brand name “Tata Power EZ Charge,” the business provides a variety of nationwide electric vehicle charging options.
In order to meet the increasing demand for EV charging services, Tata Power has installed EV charging stations at key places, such as roads, commercial centers, and public areas.
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL):
An industry leader in engineering and manufacturing, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is actively working to establish the infrastructure needed for charging electric vehicles.
For a range of uses, including home, business, and public charging, BHEL provides a comprehensive portfolio of charging options, including AC and DC chargers. The company provides EV users with dependable and effective charging options by utilizing its knowledge of power electronics and renewable energy.
ABB India:
One of the major players in the market for electric vehicle charging stations is ABB India, a division of the multinational technology giant ABB Group.
ABB serves fleet managers, owners of electric vehicles, and providers of charging infrastructure with a wide range of charging solutions, including fast chargers, ultra-fast chargers, and depot chargers.
The smooth integration of ABB’s charging infrastructure with the power grid and the swift growth of electric mobility in India are the two main goals of its design.
Fortum India:
The development and management of electric vehicle charging infrastructure in India is a major undertaking for Fortum India, a subsidiary of the Finnish energy corporation Fortum Corporation.
A network of public charging stations with fast chargers is offered by the corporation, which goes by the name “Fortum Charge and; Drive,” giving EV users dependable and easy access to electricity.
Fortum India is dedicated to advancing environmentally friendly transportation options and cutting carbon emissions with its initiatives for charging infrastructure.
Exicom Power Solutions:
With a focus on developing infrastructure for electric car charging, Exicom Power Solutions is a top supplier of cutting-edge energy storage and power conversion solutions in India.
The company provides a variety of AC and DC charging options, including as pedestal chargers, wall-mounted chargers, and rapid chargers, to accommodate the various requirements of electric vehicle owners and operators.
Modern technology forms the foundation of Exicom’s scalable, economical, and efficient charging infrastructure.
Magenta Power:
In India, Magenta Power is a leader in the provision of cutting-edge and environmentally friendly charging infrastructure solutions for public, commercial, and residential use.
The business, which goes by the name “ChargeGrid,” provides a network of intelligent charging stations with capabilities like remote monitoring, invoicing, and payment integration.
By offering dependable and easily accessible charging infrastructure, Magenta Power hopes to hasten the adoption of electric vehicles in India.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
The demand for easily accessible charging infrastructure is only going to increase as electric cars (EVs) gain popularity. To encourage the broad use of electric vehicles and advance sustainable transportation, it is essential to install charging stations for these vehicles.
Everything from site selection to commissioning will be covered in this article’s thorough installation guide for electric vehicle charging stations.
Step 1: Site Selection and Planning
Identify Suitable Locations:
Based on user demand, accessibility, visibility, and closeness to power sources, charging station locations are selected. Strategic sites include office buildings, retail malls, parking lots, and apartment buildings.
Assess Electrical Infrastructure:
Ascertain the electrical infrastructure’s capability and availability at the selected location. To determine the electrical panel’s capacity, voltage levels, and proximity to utility connections, study the site. Verify compliance with regional construction codes and standards.
Consideration for Future Expansion:
Consider the demand for EV charging in the future and make scalability plans. Select areas that have enough room for future EV adoption—such as modifications to electrical networks and additional charging stations.
Step 2: Design and Equipment Selection
Identify Suitable Locations:
Based on user demand, accessibility, visibility, and closeness to power sources, charging station locations are selected. Strategic sites include office buildings, retail malls, parking lots, and apartment buildings.
Assess Electrical Infrastructure:
At the selected location, ascertain the electrical infrastructure’s availability and capacity. To determine the capacity of the electrical panel, the voltage levels, and the distance from utility connections, do a site survey. Verify that it complies with all applicable building codes and laws.
Consideration for Future Expansion:
Consider future EV charging demand and make scalability plans. As EV use rises, pick locations with enough room for future modifications to electrical networks and extra charging stations.
Step 2: Design and Equipment Selection
Choose Charging Station Type:
Based on the demands of the user, the required charging speed, and the features of the site, choose the right kind of charging station. Level 2 chargers (AC) for residential and business use and DC fast chargers for rapid public charging are common varieties.
Determine Power Requirements:
Based on anticipated usage patterns, EV battery capacities, and charging speeds, determine the power needs for charging stations. Make that there are no circuit overloads or voltage dips as a result of the intended charging capacity being supported by the electrical infrastructure.
Select Charging Equipment:
Select charging accessories from reliable producers who abide by rules and industry requirements. Think about things like warranty coverage, compatibility with EV models, support services, and reliability.
Step 3: Installation Process
Electrical Wiring and Infrastructure:
Install the distribution equipment, conduit, and electrical wire required to link charging stations to the power supply. Respect safety regulations and electrical codes to guarantee correct installation and avoid risks.
Mounting and Placement:
Chargers should be firmly mounted to the wall or the ground using the proper mounting hardware. Make sure that the heights of the charging stations are ideal for user visibility and accessibility.
Network Connectivity:
Provide charging stations with network access to facilitate remote management, payment processing, and monitoring. Install networking devices, like modems and routers, and set up network configurations in accordance with manufacturer instructions.
Step 4: Testing and Commissioning
Electrical Testing:
To ensure appropriate wiring, voltage levels, and circuit protection, conduct electrical testing and commissioning. To guarantee electrical safety and compliance, conduct tests for ground fault protection, continuity, and insulation resistance.
Functionality Testing:
By connecting EVs and confirming charging operation, connectivity with network systems, and user interface functioning, one can test the functionality of charging stations. Determine the cause of any problems or malfunctions that arise during testing and fix them.
User Training and Education:
Give consumers instruction and resources to help them use charging stations in a safe and efficient manner. In order to guarantee a satisfying user experience, include instructions on charging protocols, payment options, and troubleshooting advice.
Step 5: Maintenance and Support
Routine Maintenance:
Create a maintenance plan that includes routine service, cleaning, and examination of the charging apparatus. Examine the equipment for indications of corrosion, loose connections, and wear and tear. Take quick action to fix any problems to avoid downtime.
Technical Support:
Assist users with technical help and assistance when they have equipment failures, connectivity challenges, or charging problems. Create a help desk or hotline to handle user questions and offer prompt support.
Software Updates and Upgrades:
Keep up with the latest firmware upgrades, security fixes, and software updates that charging station manufacturers have published. To guarantee optimum performance, dependability, and compatibility with EVs, apply updates as advised.
I am an engineer in a government department and also a blogger. I write posts on topics related to electrical and electronics engineering.
