Types of Power Plants: A Comprehensive Overview
Table of Contents
ToggleThe world depends on power plants to generate electrical energy as the fundamental source that powers residential housing as well as commercial and industrial facilities. A particular power plant transforms different energy types into electricity while maximizing the efficiency of a selected energy source for its operations. The power generation technologies, alongside fuel usage and environmental impact, as well as price point, differ substantially based on the power plant type. The article examines the types of power plants as well as their operational principles and both their advantages and notable limitations.
What is a Power Plant?
Power plants, also known as power stations, serve as facilities that produce electric energy and then transmit it to end users. Different types of power plants generate power through the usage of fossil fuels along with nuclear energy and solar power as well as wind energy and hydroelectric energy to create electrical energy.
Different types of power station have different selection preferences based on available resource availability together with environmental considerations and installation and operational costs.
The power plants send electricity through transmission lines that connect homes and businesses to provide power whenever it is required.
The growing urgency to combat climate change along with rising demands for environmentally friendly energy solutions has led the world to direct attention toward creating power plants based on renewable energy resources.
Type of power plants
Steam Power Plant

Thermal power plants serve as the dominant power generation industry throughout the entire world. A fossil fuel power station produces electrical energy through heat-based operations whose primary fuel source originates from coal oil and natural gas combustion.
The combustion heat drives the production of steam that powers turbines linked to generators through this procedure.
Working Mechanism
The production of electricity at steam power plants starts when heat energy transforms into electrical energy. The power generation process starts with fossil fuel burning in a boiler which creates high-pressure steam.
The steam flows toward a steam turbine after its generation process. The turbine blades spin through the force generated by the steam thus powering the generator which is attached to the turbine. The generator produces electricity through the rotating turbine motion.
The turbine-discharged steam moves to a condenser unit that cools the steam to liquid state then returns the water to heat it once again in the boiler for additional usage. A continuous supply of steam exists through sustained repetition of the process.
Types of Steam Power Plants
- Coal Power Plants: Thermal power generation facilities of this type constitute the majority of such plants. Fire in coal generates steam which powers turbines that activate generators.
- Oil Power Plants: The production of steam through heated oil power plants achieves their operation.
- Natural Gas Power Plants: Combined-cycle electricity production utilizes natural gas as one of its main fuel sources. The combined-cycle power plant uses natural gas in its gas turbine to produce electricity while the turbine waste heat generates supplemental power in a steam turbine.
Advantages
- Reliable and Consistent Energy Supply: Because power plants produce stable and interrupted electrical power, they function effectively as base-load power generators.
- Established Technology: Steam power plants operate using mature technology fundamentals which engineers have used at their disposal over numerous decades.
- Flexibility in Fuel Sources: Thermal power generation facilities can operate with different fuel types including coal, natural gas and oil thus providing adaptability in power supply alignment with available resources and pricing patterns.
- Large-Scale Generation: These power facilities generate abundant electric output which enables them to be the key providers of energy for big cities together with industrial facilities.
Disadvantages
- Environmental Pollution: Greenhouse gas emission from steam power plants involves substantial carbon dioxide (CO2) releases that advance climate change effects. The emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) severely pollutes the airspace and produces acid rain.
- High Fuel Consumption: Due to their reliance on fossil fuels steam power plants negatively impact both natural resource availability and affect the energy market stability through price fluctuations.
- Water Usage: The heat-generating process demands large water quantities for cooling purposes and thus places excessive strain on nearby water supplies when operating in dry areas.
- High Operational Costs: The dependence of fossil fuels in the energy sector causes volatile fuel market prices and continual expenses toward fuel acquisition which causes instability in long-term operational costs.
Solar Power Plant
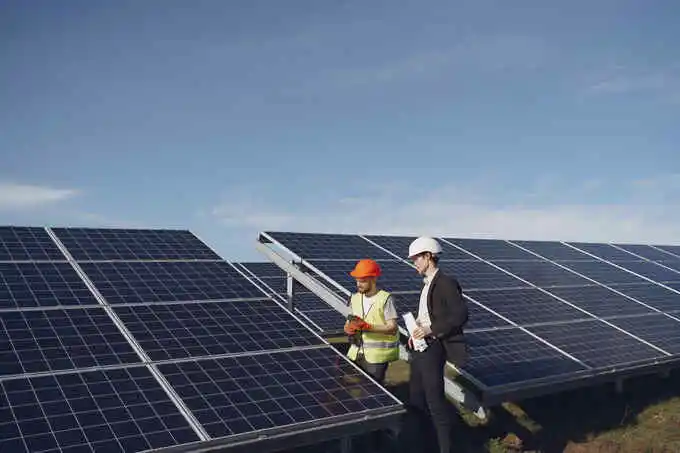

The process of electricity generation in solar power plants depends on the conversion of sunlight into energy. Photovoltaic (PV) power plants together with Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants comprise the two classifications of solar pv power plants.
A PV plant produces electrical power by applying sunlight through photovoltaic cells in solar panels yet CSP plants generate electricity from sunlight using mirrors paired with lenses to create heat-evoked energy production.
The usage of solar pv plants develops clean renewable electricity which decreases our dependence on conventional fuel sources.
Working Mechanism
Solar Power Plants : The semiconductor-based solar panels known as silicon operate in PV plants to generate electricity by converting sunlight. The photovoltaic cells generate electricity after sunlight causes their material electrons to become activated.
The conversion of direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) becomes possible through the use of an inverter, which makes it suitable for connecting to electrical grids.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Plants: The central receiving area of CSP plants becomes heated by sunlight which passes through mirrors or lenses.
The focused sunlight produces steam through the heating of a fluid, usually molten salt. The system utilizes the heated steam to power turbines connected to electric generators.
Stored heat inside CSP facilities enables the system to generate electricity during both sunlight hours and dark periods.
Advantages
- Renewable and Sustainable: The continuous availability of solar power extends over billions of years since it represents a renewable source offering long-term energy solutions.
- Environmentally Friendly: During operation renewable energy power plants release no greenhouse gases which makes them rank among the most environmentally friendly power sources. The production of solar power plants contributes to the reduction of climate change together with air quality improvement.
- Low Operating Costs: Solar energy plants demand minimal expense in upkeep and operations after their first implementation stage exceeds the costs of fossil fuel production facilities.
- Energy Independence: The use of solar power helps nations break their energy dependence on foreign fuel supplies which strengthens both national and community energy security.
- Scalable and Versatile: Solar power provides flexibility through installations that range from residential rooftops to massive utility facilities and it operates in diverse locations.
Disadvantages
- Intermittency: Solar power production depends on sunlight availability because both night-time and cloudy conditions prevent solar energy generation. The fluctuating nature of solar power supply presents challenges to power grid stability, but adequate energy storage solutions prevent these challenges.
- High Initial Costs: The financial barriers for solar power plant construction especially concerning large-scale projects include high initial setup expenses. Utilities face a high challenge when it comes to paying for initial installation expenses because operating expenses remain affordable for them.
- Space Requirements: Major solar facilities occupy large territories of land in order to function effectively. Dense population areas along with areas with limited free space create difficulties for solar power installation.
- Efficiency: Photovoltaic cells only operate with 15-20% efficiency thus large areas of land are needed to produce substantial electrical power.
Nuclear Power Plants

Base load power plant combine nuclear fission for heat production to create electricity through this process.
Nuclear fission creates atomic nucleus decomposition that generates significant energy output from splitting atomic nuclei. The generated energy produces steam that activates turbines to power up generator systems.
Working Mechanism
Base load power plants harness uranium-235 or plutonium-239 atomic elements as their primary sources of fuel. Nuclear fission occurs when these atoms accept neutrons, which results in powerful heat emissions.
The product heats the steam from the water to rotate connected turbine generators. The plant uses the produced steam to drive turbines before condensing it for repetition of this cycle.
Advantages
- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Nuclear power plants operate with minimal pollution which transforms them into an eco-friendly electric power generation method that does not substantially increase global warming effects.
- High Energy Output: The fuel spent in a small capacity can generate substantial electrical energy. The vast amount of created energy from base load power plants enables them to deliver uninterrupted power for extensive populations.
- Reliable Power Supply: The operational capabilities of nuclear facilities can maintain continuous electricity supply over long periods because these facilities achieve high levels of power output.
- Energy Independence: Through the generation of nuclear power nations gain independence from buying foreign fossil fuels which builds their national energy security.
Disadvantages
- Radioactive Waste Disposal: The security of nuclear waste stands as a major hurdle because this dangerous material survives for extended millennia. Sustained storage solutions delivering absolute safety remain both expensive to implement and present an existing storage challenge.
- High Initial Costs: Building base load power plants demands enormous initial capital expenses for constructing the facility together with maintenance safety elements and contractual requirements leading to high construction costs.
- Nuclear Accidents: Nuclear power operations result in catastrophic risks because of incidents such as Chernobyl and Fukushima which combine exposure to harmful radiation with devastating environmental contamination.
- Limited Fuel Supply: Uranium as the fuel source for nuclear power serves as a limited supply that might become unsustainable as we progress toward a longer duration of energy requirements.
Hydroelectric Power Plants
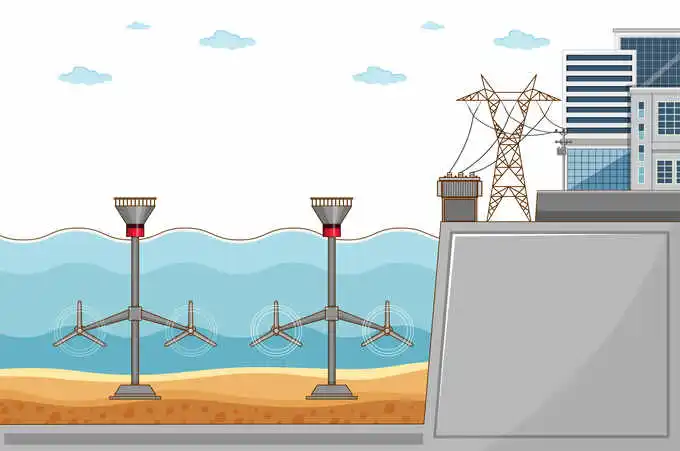
Water energy at hydroelectric power plants creates electricity through the use of flowing water momentum.
Power generation using hydroelectric techniques occurs either through water reservoir storage achieved with large dams or by capturing the moving energy present in rivers.
Working Mechanism
A standard hydroelectric power generating facility uses penstock water releases to activate turbines.
Water pressure on the turbines makes them rotate while generators generate electrical power through their connection to the turbines.
The generator produces electricity by turbine rotation. After undergoing the process the water travels back to the river at its downstream section.
Types of Hydroelectric Plants
Reservoir (Storage) Hydroelectric Plants: The plants create substantial water storage facilities by building reservoirs that use dams as their foundations. The water outlet proceeds as a directed release for electricity production.
Run-of-River Hydroelectric Plants: These plants operate without the necessity for dams while creating minimal harm to the environment. The natural river currents provide the power needed to create electricity in these facilities.
Pumped Storage Hydroelectric Plants: Two different elevation-based reservoirs are utilized by these plants. A system moves water from a lower reservoir to a higher storage point during times of weak electricity consumption, so power production can occur at peak usage periods.
Advantages
- Renewable Energy Source: Hydroelectric power functions as a renewable energy technology because it depends on the regular water cycle which provides ongoing sustainability to power generation.
- Low Emissions: The amount of greenhouse gases released to generate power from hydroelectric plants remains significantly lower than those produced when using fossil fuels.
- Reliable Power Supply: The energy supply from hydroelectric plants remains stable and fulfills customer demands while responding instantly to changes in demand rates.
- Long Operational Life: The operational period of hydroelectric plants extends very long while their operational expenses remain reasonably low.
Disadvantages
- Environmental Impact: When dams are built they create disturbances within local biological habitats as well as harm water-dwelling organisms and block animal migration routes.
- High Initial Costs: Significant capital expenditure stands as a primary requirement for constructing a hydroelectric plant.
- Dependence on Water Availability: The amount of energy that can be generated from water depends heavily on the seasonal changes in water flow rates particularly in regions with dry conditions.
Wind Power Plants
The production of electrical energy relies on the process that turns wind-driven kinetic energy into electrical power through wind power plants. Multiple wind bines placed in nearby locations from wind farms to extract power from moving air.
Working Mechanism
Wind turbines possess enormous rotating blades which the passing wind powers. The rotating blades transform into motion a generator which is connected to a rotor.
The electrical energy production occurs when the generator transforms the mechanical blade rotations into electricity.
Wind power plants find their placement across both terrestrial ground (onshore) and floating offshore locations because wind speeds reach higher speeds in the maritime area.
Advantages
- Renewable and Sustainable: The nature-driven pattern of wind allows wind power to serve as a permanent renewable energy solution which preserves current resources for sustained electricity production.
- Low Operating Costs: The maintenance and operation expenses for wind power plants remain low after their installation because these facilities operate efficiently throughout their operational period.
- Clean Energy Source: The electricity generation process of wind power creates zero greenhouse gases which both decrease pollution levels and lessen climate change impacts.
- Scalable and Flexible: Wind power plants feature scalability which lets operators choose between small onshore machines serving individual homes and large offshore wind power stations that fulfill various energy requirements.
- Job Creation: The wind energy industry supports employment creation in manufacturing operations and installments and maintenance tasks that advance national economic development.
Disadvantages
- Intermittency and Variability: Wind power constitutes a form of energy production that relies on weather variations since it cannot be accessed during still conditions and nighttime.
- Visual and Noise Impact: The industrial presence of wind turbines produces disruptive noises that disrupt neighborhoods while damaging wildlife ecosystems and creating a visual disturbance within local surroundings.
- Land Use and Wildlife Disruption: Wind farms occupy broad stretches of territory thus creating potential harm to flying animals and their surroundings through improper turbine placement.
- High Initial Costs: Initial expenses for wind turbine deployment are substantial especially for offshore applications but decreasing technology prices help lower installation costs.
Conclusion
The global power sector includes multiple utility plants which power their operations through different energy resources.
Thermal and nuclear power plants administer the worldwide power sector yet renewable sources of energy especially wind power solar energy and hydroelectric generation demonstrate quick development in electricity generation volumes.
The advantages and limitations of different types of power plants require power generation developers to weigh environmental costs against resource reserves and enduring sustainability when selecting power plant technologies.
The necessity to combat global warming and establish greener clean energy solutions is driving power stations toward more ecologically friendly multiple power generation systems.
I am an engineer in a government department and also a blogger. I write posts on topics related to electrical and electronics engineering.
