What is Electric Current And How Does it Work?
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Electric Current
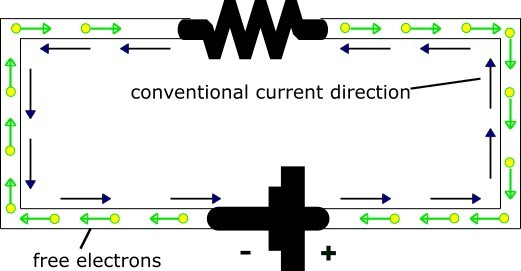
the flow of electric current takes place by the movement of the electrons in a conductor.it can also be called as the rate of movement of electrons is known as electric current.in other words an electrons is defined as the quantity of electric charge transported per unit time
electric current = rate of flow of electrons
one passes the quantity of electricity from the section of the conductor at a given time is equal to the product of rate of movement of electrons and time.
The flow of electrons in any conducting material is called electric current.these electrons which carry current in any conducting material are called free electrons or charged electrons.now this question arieses in our mind that the number of electrons and protons in any atom is same,that is,the atom is neutral.
How do electrons get charged ?
now electrons are charged only when some electrons are removed from neutral atom or supplied extra electrons to the atom.we know from electron theory that the number of electrons in a atom is more then the number of protons,then the atom is negatively charged.
again if the number of electrons is less than the number of protons,then the atom becomes positively charged.only the electrons in this positively and negatively charged atom are responsible for carrying the electric current.
it is also worth nothing that the electrons of the outer end of the atom of any conducting material can be easily removed by applying a little force,but the protons located in the nucleus in atom bound to very powerful forces is called the nuclear binding energy.
for this reason it is difficult to removed protons from the nucleus.the higher the energy of the electrons,the less force is needed to remove them from the atom.
due to this property,some substances are very good conductors of electricity,in which electric current flows through.the more free electrons a subtance has,the better it is for flow of current.
for example silver,gold,copper,aluminium is a good material for carrying electric current.we have learned that what is electric current and who is responsible for carrying it,but now we have to know who is responsible for carrying free electrons in any conducting material.
current is a scalar quantity.in a conductor,the current flow indicate by an arrow.such indication only show direction of flow of charges in a conductor.this is the direction which positive charge move.
one thing to note is that the power of the current will depend on the flow of charge per unit time.
Drift Velocity
when the free electrons come in contact with the electric field,the average velocity of the free electrons comes,this velocity is called drift velocity.
the drift velocity of free electrons is about 10^{-5}ms^{-1}.drift velocity is only responsible for electric current in the metal.
the flow of current in a conductor is directly proportional to the drift velocity of free electrons.
small drift velocity of free electrons give rise to sufficient current because in any conductor number of free electrons is very large.
the relation between current and drift velocity by this formula.
I=neAv_{d}
where I = electric current in conductor
n = number of electrons per unit volume.
e = charge on each electron.
v_{d} = drift velocity of free electrons.
Potential Difference
potential difference is responsible for carrying free electrons in a conducting material.now first of all know what is electric potential after that you will know about potential difference.
when a body is charged,the work that has to be done during charging is stored in the form of potential energy in the work body.the ability of this charged body to do work is called electric potential.
electrical potential\left(V\right)=\dfrac{work done\left(W\right)}{charge\left(Q\right)}
if two bodies have different electric potential,a potential difference exists between the bodies.for example two bodies X and Y having potentials of 10 volts and 15 volts respectively.

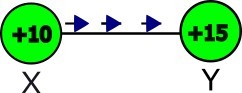
when this two bodies are connect through a conductor then electrons will flow from body X to body Y.
when both the bodies reach the same potential,the flow of electrons stops.also flow of electric current stops.this lets us know that current will flow in a circuit if potential difference exists.
that means no potential difference no current.in other words,potential difference is also called voltage.to maintain the potential difference in a circuit,a force is required which is called electromotive force(emf).
an emf is a Cell or energy source that maintains a potential difference in a circuit.for example cell,generator that maintains a potential difference.
some important things to note that electric current does not flow due to emf.emf maintain electric potential difference and potential difference causes electric current to flow.
although emf and potential difference both are measured in volts.as a result we have come to the conclusion that due to potential difference,the movement of free electrons is from negatively charged atoms to positively charged atoms.this flow of free electrons is called electric current.
Ampere
in practice coulomb is used as the unit of charge.one coulomb of charge is equal to the charge on 6\cdot 25\times 10^{16} electrons.
when one coulomb of charge moves past a single point in one second,it is called an ampere(A).the ampere is named for the french physicist Andrae Marie Ampere.ampere is unit of current.
the relation between ampere and coulomb per second is
Ampere\left(I\right) = \dfrac{coulomb\left(Q\right)}{second\left(t\right)}
Voltage
voltage is the force that flow the electrons in the circuit.the unit for measuring voltage is the volt.volt the unit of voltage,was named after the great scientist Alessandro Volta.
Type of Electric Current
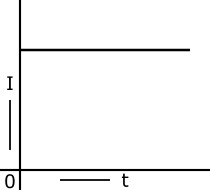
Steady Current -
when the magnitude of current does not change with time,it is called a steady current.steady current is also called direct current(D.C.)
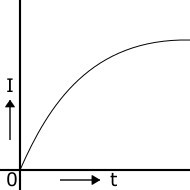
Varying Current -
when the magnitude of current changes with time it is called varying current
Alternating Current -
when current flowing varies in magnitude and direction periodically,it is called alternating current.

I am an engineer in a government department and also a blogger. I write posts on topics related to electrical and electronics engineering.
