Vacuum Circuit Breaker : Working Principle and its Application
Table of Contents
ToggleCircuit breaker is a safety switching device of the electrical system, with the help of which the circuit is off at fault or on-off as per requirement in normal condition. Vacuum medium technology was first used in the 1960s to interrupts an electric circuits at faults. This article will discuss in vacuum circuit breaker working principle, different types, application, parts, advantages and disadvantages.
What is Vacuum Circuit Breaker ( VCB )

VCB full form in electrical, vacuum circuit breaker. This circuit breaker is a type of switchgear device used to break and control the fault current.
In this breaker vacuum is used for arc extinction medium. A vacuum port for the vacuum inside which the fixed and moving contacts are completely sealed.
When the circuit breaker opens during fault, it separates the contacts and generates an arc, which is quickly extinguished in the vacuum. The port inside which the arc is extinguished is also called vacuum interrupter.
Vacuum Curcuit Breaker Working principle
Operating principle
Working principle of vcb is that the arc is formed in the vacuum and the process of extinguishing it is quite quick.
When the circuit breaker opens, an arc is formed between the static and moving contacts.
This arc is maintained in the vacuum interrupter, and it is extinguished very quickly because the vacuum is ion-deficient. This improves the breaking capacity and operating speed.
Arc quenching through vacuum is superior as it offers highest insulating strength.
Arc Quenching Process
When the contacts are open inside the vacuum pot an arc is produced due to ionisation vapour between contacts. Intensely hot spot is generated due to high current density during opening of contacts.
the arc is quickly extinguished because the important properties of vacuum to assist arc extinction and prevent restriking. Arc extinguishing in vacuum breaker is generally based on the material and shape of the contacts and the technique of condensing of metal vapour.
The path of interrupted current in vacuum is very short, so the arc splits into many parallel paths. The total current in the path is divided into many parallel arcs which repel each other and spread over the surface of the contacts. Eventually the arc diffuses and extinguishes immediately.
Types of VCB ( Vacuum Circuit Breaker )
There are many types of vcb, which are chosen based on different applications and requirements.
Outdoor Vacuum Circuit Breaker
Outdoor types of vcb are mainly used in outdoor power distribution systems. These breakers are installed in high voltage lines and sub-stations, where they play a vital role in breaking external fault currents and keeping the system safe.
Indoor Vacuum Breaker
Indoor types of vcb are mainly used in indoor power distribution systems. These breakers are used to protect high voltage equipment and systems where there is no influence of the outdoor environment.
Medium Voltage Vacuum Circuit Breaker
Medium voltage VCBs are mainly used in the voltage range between 1 KV to 36 KV. These breakers are suitable for industrial and commercial applications where medium voltage systems are used.
High Voltage Vacuum Breaker
High voltage VCBs are mainly used in voltage ranges above 36 KV. These breakers are used in high voltage transmission lines and sub-stations where safety of high voltage systems is important.
Applications of VCB
VCBs are used in various power distribution and protection systems. Due to its high performance, reliability, and low maintenance requirements, VCB breaker are preferred in several critical applications. In this article, we will discuss in detail the various applications of VCBs.
1. Power Distribution System
High Voltage Sub-Stations in Power Distribution System
Vacuum breaker are used in high voltage sub-stations. These sub-stations are important for transmitting electrical power from the generating locations to the consumer areas.
VCB circuit breaker have the capability to break high voltage faults rapidly and safely, thereby ensuring the safety of the power network.
Medium Voltage Distribution Network
In medium voltage distribution networks, VCB circuit breaker are used for the distribution of electrical power to the consumers.
These breakers ensure the safety of the distribution network by rapidly breaking the fault currents. Apart from this, VCBs are also used to protect transformers and other distribution equipment.
2. Industrial Applications
In factories and production units
Vacuum breaker are used in a wide variety of factories and production units. These breakers ensure the safety of high voltage equipment and machines, so that the production process is not interrupted.
VCBs are used to protect motor control centers, power distribution units, and other critical equipment.
Mining Industry
In the mining industry, VCB breaker are used to protect high voltage equipment. The use of high voltage equipment is common in the mining industry, and in case of faults VCBs are used to quickly and safely break the fault currents. This ensures the safety of mining equipment and workers.
3. Commercial Applications
In commercial buildings and offices
In commercial buildings and offices, Vacuum breaker are used to protect the electrical distribution system.
These breakers ensure the safety of high voltage equipment and distribution networks, so that business operations continue without any interruption.
Shopping malls and multiplexes
In large commercial complexes such as shopping malls and multiplexes, VCBs are used to protect the high voltage distribution system.
These breakers ensure the safety of the electrical network by breaking fault currents rapidly, thereby ensuring the safety of customers and employees.
4. Transport sector
Railways
In the railway system, VCB breaker are used to protect traction substations and electric trains. These breakers have the capability to break high voltage faults rapidly and safely, allowing rail traffic to continue running without any disruption.
Metro systems
In metro systems, Vacuum breaker are used to protect traction systems. Metro trains use high voltage systems, and VCBs are used to ensure the safety of these systems. This ensures the safety of metro passengers and equipment.
5. Power generation
Thermal power plants
In thermal power plants, VCB breaker are used to protect power generation units. These breakers ensure the safety of generation equipment by rapidly breaking fault currents, thereby ensuring power generation continues without interruption.
Hydro Power Plant
In hydropower plants, VCBs are used to protect hydro generation units. These breakers have the capability to rapidly and safely break high voltage faults, thereby ensuring the safety of the hydropower generation system.
6. Renewable Energy
Solar Power Plant
In solar power plants, vacuum breaker are used to protect solar panels and other high voltage equipment. These breakers ensure the safety of solar power generation by rapidly breaking fault currents, thereby ensuring continuous and safe power generation.
Wind Power Plant
In wind power plants, VCB circuit breaker are used to protect wind turbines and other high voltage equipment. These breakers have the capability to rapidly and safely break high voltage faults, thereby ensuring the safety of the wind power generation system.
Components of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
VCB is a complex device having many critical components that contribute to its functioning and operation. Correct and coordinated functioning of these components ensures the effectiveness and reliability of the VCB breaker.
1. Vacuum Interrupter
The vacuum interrupter is the most important component of the vacuum breaker. It is a sealed chamber having two contacts: static contact and dynamic contact.
The main function of the vacuum interrupter is to break and extinguish fault currents.
Functioning
When the circuit breaker opens, the dynamic contact separates from the static contact, producing an arc.
This arc is produced within the vacuum interrupter and is extinguished very quickly as the vacuum lacks ions. This process is very fast, allowing fault currents to be controlled effectively.
2. Static and Dynamic Contacts
Static Contact
The static contact is located at one end of the vacuum interrupter and remains stationary. This contact is a part of the electrical circuit and plays a vital role in conducting fault currents.
Moveable Contact
The moveable contact is located at the other end of the vacuum interrupter and is moveable. When the circuit breaker opens or closes, this contact separates or connects with the static contact.
The speed and stability of the dynamic contact have a significant impact on the effectiveness of the circuit breaker.
3. Arc Shield
The arc shield is a vital component that protects other components from the heat and other effects generated when the arc is formed inside the vacuum interrupter.
This shield helps to control and limit the arc, thereby increasing the efficiency and safety of the breaker.
4. Driving Mechanism
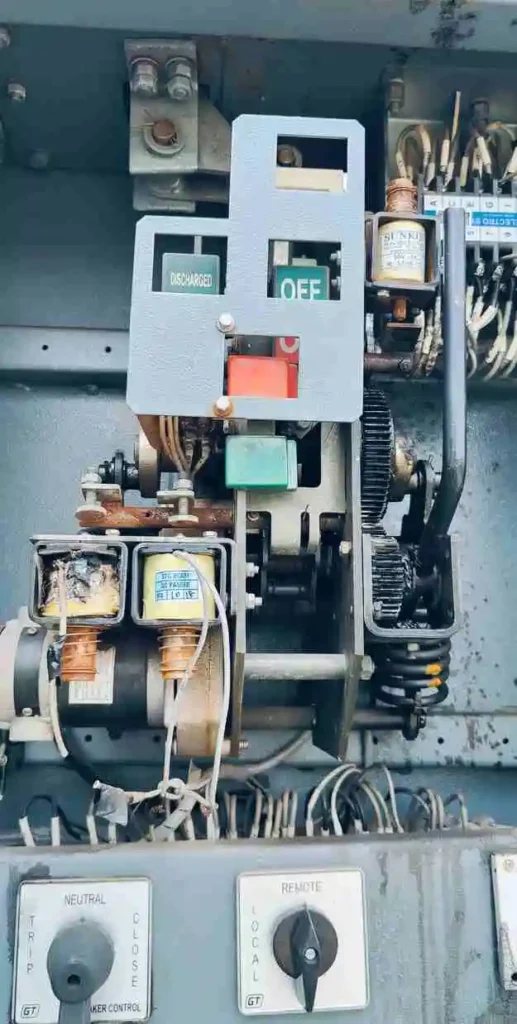
The driving mechanism is the mechanism that is responsible for opening and closing the circuit breaker. This mechanism may be driven through electric motors, springs, or electromagnetic coils.
Types
Spring Operated Driving Mechanism: This type of mechanism uses springs that provide energy to open and close the vacuum breaker.
When the springs are compressed, they store energy, which is later used to operate the circuit breaker.
Motor Operated Driving Mechanism: This mechanism uses electric motors that provide energy to open and close the circuit breaker. Motor operated mechanisms are suitable for fast and precise operation.
5. Control and Protection Mechanism
Control mechanism
The control mechanism is used to control and monitor the operation of the circuit breaker. It consists of control panels, relays, and switches, which provide commands to open and close the circuit breaker.
Protection Mechanism
The protection mechanism is designed to protect the circuit breaker from fault currents. It consists of overcurrent relays, undervoltage relays, and other protection devices, which help to operate the circuit breaker by detecting fault currents.
6. Insulator

Insulators are used to keep the various components of the circuit breaker electrically isolated. These play a vital role in controlling and isolating high voltage, thereby increasing the safety and reliability of the circuit breaker.
7. Bus bars
Busbars are a key component that helps distribute electrical current to various parts of a vacuum breaker. These are high-capacity conductors that play a vital role in conducting electrical current smoothly and safely.
8. Connectors
Connectors are used to interconnect various components of a circuit breaker. These ensure that electrical current can flow without interruption. The quality and reliability of connectors are crucial in the operation of a circuit breaker.
Advantages of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The VCB breaker has many advantages, which make it an important device in the power distribution system.
High operating speed
The operating speed of a vacuum breaker is very high, which enables it to break fault currents quickly and keep the system safe. This high speed is important for the safety of electrical equipment and systems.
Low maintenance
VCB circuit breaker require very little maintenance as no oil or gas is used. Also, there are no mechanical contacts inside the vacuum interrupter, which reduces the chances of wear and tear.
Environmentally friendly
VCB are environmentally friendly as there is no emission of harmful gases. In contrast, oil and SF6 gas based circuit breakers emit harmful gases, which are harmful to the environment.
High reliability
The reliability of a vacuum breaker is high, making it a reliable device in the power distribution system. Its high breaking capacity and operating speed make it suitable for various applications.
Disadvantages of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
VCB is an important electrical safety device, which is used in various electrical systems. Although VCB breaker has many advantages, it also has some disadvantages. we will discuss the major disadvantages of VCB.
1. High initial cost
The initial cost of this breaker is often higher than fuse or other conventional circuit breakers. This high cost is especially important when large scale devices are required, such as in industrial or commercial setups.
2. Complexity and design
The design and manufacture of vcb is complex. It involves vacuum interrupters and other special components, which require correct and coordinated functioning. This complexity creates the need for more time and expertise in its operation and maintenance.
3. Limited current rating
The current rating of vacuum breaker can be limited. This can be a problem especially in high current applications, where circuit breaker with high current rating is required.
4. Maintenance Requirements
VCB circuit breaker require regular maintenance, which demands time and resources. This includes cleaning the contacts, checking the insulators, and regular checking of the condition of the vacuum interrupter.
5. Sensitivity to Operating Environment
VCBs can be sensitive to filthy or dusty environments. This can affect their performance and increase the need for regular cleaning and inspection.
6. Failure of Vacuum Interrupter
Failure of the vacuum interrupter can be a significant concern. If a fault develops in the vacuum interrupter, the functioning of the entire circuit breaker may be affected. Replacement of the vacuum interrupter can be costly and time-consuming.
7. Limitations in High Voltage Applications
Although vacuum breaker are very effective in medium voltage applications, they may have limitations in high voltage applications. Other types of circuit breakers may be more suitable for high voltage breaking.
8. Training and Expertise Required
Proper operation and maintenance of vcbs require proper training and expertise. Without proper training, errors in operation may occur, which may endanger safety.
9. Initial Commissioning Complexity
The initial commissioning process of a vcb breaker can be complex. It requires special equipment and expertise to install and test it correctly.
10. Thermal and Mechanical Stress
The ability of a VCB circuit breaker to withstand thermal and mechanical stress may be limited. Excessive thermal and mechanical stress may affect its functioning and reliability.
VCB Testing
The purpose of testing a vacuum breaker (VCB) is to ensure its functioning, reliability, and safety. Regular tests and inspections ensure that the circuit breaker is able to effectively break fault currents and protect electrical systems. We will discuss the major testing procedures of vacuum circuit breaker.
1. Visual Inspection
External Inspection
- Check for any cracks, breaks, or other visible damage to the external parts of the circuit breaker.
- Ensure that all connections and terminals are securely and firmly connected.
- Check all labels and indicators to ensure that they are clear and readable.
Internal Inspection
- Check the internal components of the circuit breaker, such as contacts, arc chamber, and insulators.
- Clean any dust and dirt accumulated on the internal components.
2. Mechanical Testing
Operating Mechanism Test
- Open and close the circuit breaker several times and see that it is operating smoothly and correctly.
- Lubricate all moving parts of the operating mechanism with suitable lubricant.
Interlock System Test
Make sure the interlock system is functioning correctly, and all safety interlocks are activated.
3. Electrical Test
Contact Resistance Measurement
Measure the contact resistance between the static and moving contacts. High resistance may indicate poor contact.
Insulation Resistance Measurement
Insulation Resistance Check: Measure the insulation resistance of the circuit breaker using an insulation resistance measuring device. Low insulation resistance may indicate damage or deterioration of insulation.
Hi-pot test
High voltage test: Test the vacuum breaker at high voltage to ensure that it can handle high voltage without any breakdown.
4. Vacuum interrupter test
Checking vacuum degree
Check the vacuum degree of the vacuum interrupter. Repair any deterioration immediately or replace the interrupter.
Checking arcing distance
Ensure that the arcing distance between contacts is correct and in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications.
5. Operating test
Operating cycle test
Test the operating cycle of the circuit breaker, including opening and closing it completely. Ensure that it is functioning smoothly and correctly.
Measure the opening and closing times and compare with the set standards. Correct any abnormalities.
6. Thermal test
Thermal Imaging
Check the temperature profile of the circuit breaker using a thermal imaging camera. Locate and correct any hotspots.
7. Functional Testing
Load Breaking Capacity
Test the load breaking capacity of the circuit breaker and ensure it is functioning correctly.
Fault Current Breaking Capacity
Test the fault current breaking capacity of the vacuum breaker and ensure it is functioning correctly.
8. Updating and Documentation
- Record all tests and inspections and update the maintenance log.
- Document any problems found and their corrective actions.
Conclusion
Knowing the working principle of vacuum circuit breaker shows how useful device it is in the electrical system. It protects power stations, transmission, distribution as well as human lives. Due to its safety and importance, domestic demand has also increased along with commercial demand.
I am an engineer in a government department and also a blogger. I write posts on topics related to electrical and electronics engineering.
